Diode Resistance Formula
Ideally speaking a diode is expected to offer zero resistance when forward biased and infinite resistance when reverse biased. R d dv d di d.
Solved It Is My Lab Report But I Couldn T Figure Out How

Load Resistance Determination In Zener Diode Electrical

Zener Diode Series Resistor Calculator
However no diode allows electric current completely even in forward biased condition.

Diode resistance formula. I have this problem with a diode and a series resistance next to it. Change the saturation current and watch the changing of iv curve. In electronics diode modelling refers to the mathematical models used to approximate the actual behaviour of real diodes to enable calculations and circuit analysis.
Hence diode resistance can be defined as the effective opposition offered by the diode to the flow of current through it. The diode equation is plotted on the interactive graph below. The thermal voltage of the diode is approximately 25mv at 300k which is a temperature that is very close to room temperature.
N ideality factor a number between 1 and 2 which typically increases as the current decreases. The ac resistance of the diode is increased by lowering the q point of operation. I is the current through the diode i s is the reverse saturation current v is the voltage across the diode can be positive or negative n is a junction constant typically around 2 for diodes 1 for transistors.
A p n junction diode allows electric current in one direction and blocks electric current in another direction. The opposition offered by a diode to the direct current flowing forward bias condition is known as its dc forward resistance or static resistance. This resistance is a parasite resistance rs.
In short it is equivalent to slope of voltage current of the pn diode. The standard equation for current through a diode is. The resistance of diodes is equal to the below formula.
I i s exp vnktq 1 eq. A diode s i v curve is nonlinear it is well described by the shockley diode law. It is measured by taking the ratio of dc voltage across the diode to the dc current flowing through it.
The shockley diode equation or the diode law named after transistor co inventor william shockley of bell telephone laboratories gives the iv current voltage characteristic of an idealized diode in either forward or reverse bias applied voltage. The forward resistance is classified as static forward resistance and dynamic forward resistance. They ask me to calculate an expression for the diode current in function of the diode voltage.
It allows electric current when it is forward biased and blocks electric current when it is reverse biased. Diode resistance is equal to the thermal voltage vt divided by the current id passing through the diode. Static or dc forward resistance.
If the input signal is sufficient enough to produce a large swing then the resistance related to the diode for this region is called as ac average resistance. For actual diodes the expression becomes.

Diodes

Lessons In Electric Circuits Volume Iii Semiconductors

Dc Diode Calculation

Diode Characteristics Dynamic Resistance Transition Time

Diode Approximations Explained

Diode Characteristics Dynamic Resistance Transition Time

Electrical Study Notes Diode Resistance And Current

Diode Resistance Explained
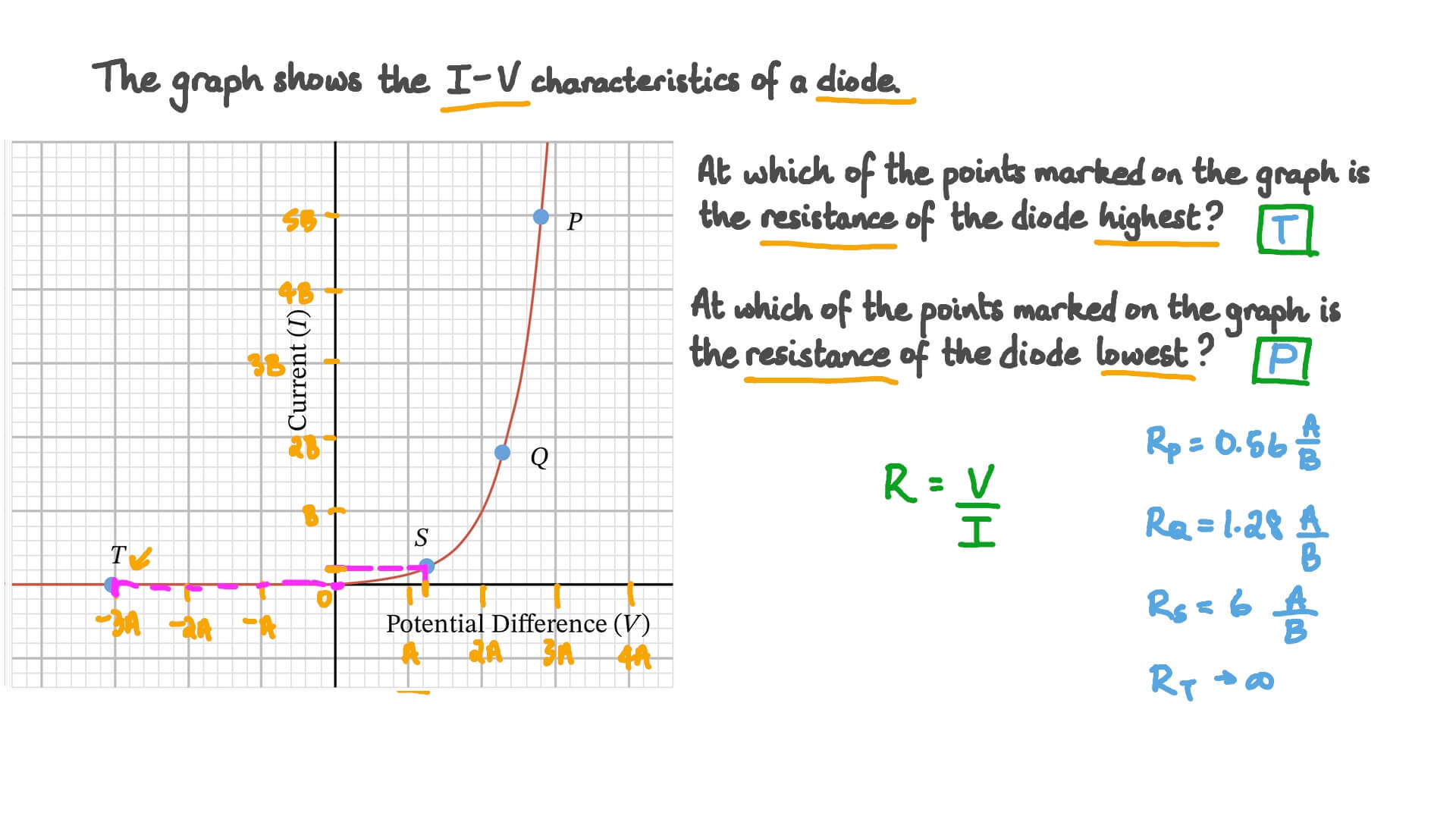

Diodes

Zener Diode Maximum Current Calculation Based On Max Rated

Diode Characteristics Dynamic Resistance Transition Time
Comments
Post a Comment